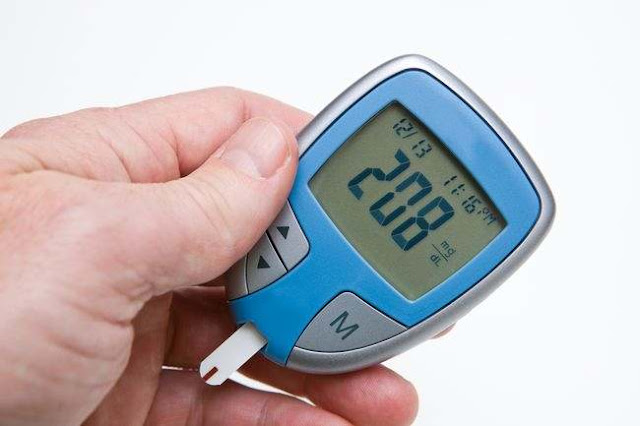
Blood Sugar Levels - Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding high blood sugar levels. In this article, we delve deep into the intricacies of what high blood sugar means, its causes, symptoms, complications, and most importantly, how to manage it effectively. Whether you're someone newly diagnosed with diabetes or seeking to enhance your knowledge on this crucial health topic, you're in the right place.
What is High Blood Sugar?
High blood sugar, medically termed hyperglycemia, occurs when there is an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream. Glucose is the primary source of energy for our cells, and it comes from the foods we consume, primarily carbohydrates. However, when the body fails to properly utilize or produce insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia.
Causes of High Blood Sugar
Understanding the causes of high blood sugar is essential for effective management. Several factors can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, including:
1. Poor Diet
Consuming foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can spike blood sugar levels rapidly. Processed foods, sugary beverages, and sweets can all contribute to hyperglycemia.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps the body utilize glucose more efficiently by increasing insulin sensitivity. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to insulin resistance, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
3. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in higher blood sugar levels. This condition is often associated with obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise.
4. Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and antipsychotics, can interfere with insulin function and lead to hyperglycemia.
5. Stress
Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can cause blood sugar levels to rise temporarily. Chronic stress may contribute to long-term hyperglycemia.
Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
Recognizing the symptoms of high blood sugar is crucial for prompt intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss
- Slow wound healing
- Frequent infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have risk factors for diabetes, such as a family history or obesity, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Complications of High Blood Sugar
Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Some potential complications include:
1. Cardiovascular Disease
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
2. Kidney Damage
Chronic hyperglycemia can impair kidney function and lead to kidney disease or kidney failure.
3. Nerve Damage
Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a common complication of diabetes resulting from high blood sugar levels. It can cause numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities.
4. Vision Problems
Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss or blindness if left untreated.
5. Foot Complications
Peripheral neuropathy and poor circulation associated with diabetes can increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections, which may ultimately require amputation.
Managing High Blood Sugar
Managing high blood sugar requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle modifications. Here are some strategies to help keep blood sugar levels in check:
1. Healthy Diet
Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fresh fruits and vegetables. Limit your intake of sugary, processed foods, and refined carbohydrates.
2. Regular Exercise
Engage in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercise, strength training, or yoga, to improve insulin sensitivity and help control blood sugar levels.
3. Medication Adherence
Take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider, including insulin or oral medications to help manage blood sugar levels.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood sugar monitoring can help you track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
5. Stress Management
Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, to help keep stress levels in check and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Conclusion
Understanding high blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By implementing lifestyle modifications, adhering to a healthy diet, staying physically active, and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and lead fulfilling lives.